Country Intelligence
ASIA
- 1016 Companies from 25 Countries.
- Average defence spending for the region is 2.60% of the GDP
- 14 Countries employing Offsets/IC
EUROPE
- 1341 Companies from 34 Countries.
- Average defence spending for the region is 1.63% of the GDP
- 15 Countries employing Offsets/IC
LATIN & CENTRAL AMERICA
- 625 Companies from 12 Countries.
- Average defence spending for the region is 2.43% of the GDP
- 2 Countries employing Offsets/IC
NORTH AMERICA
- 171 Companies from 3 Countries.
- Average defence spending for the region is 2.14% of the GDP
- 2 Countries employing Offsets/IC
OCEANIA
- 65 Companies from 2 Countries.
- Average defence spending for the region is 1.56% of the GDP
- 2 Countries employing Offsets/IC
AFRICA
- 106 Companies from 10 Countries.
- Average defence spending for the region is 2.40% of the GDP
- 6 Countries employing Offsets/IC
Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
- 526 Companies from 6 Countries.
- Average defence spending for the region is 4.98% of the GDP
- 6 Countries employing Offsets/IC
Tenders
Offset News
Offsets / IC
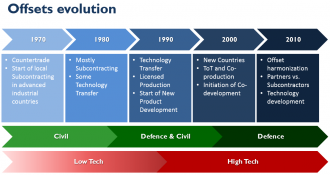
Offsets/Industrial Cooperation (IC) is the umbrella term for a broad range of industrial and commercial compensatory practices demanded as a condition for acquisition of strategic military or civil equipment. Offsets are officially or unofficially used by more than 90 governments today, while more and more countries recognise the benefits that a structured offset policy can bring to the economy. Each country has its own regulatory framework regarding Offsets/IC, with varying degrees of complexity. Offsets/IC are generally associated with major Aerospace and Defence (A&D) contracts from foreign suppliers. Programs are negotiated between prime contractors and governments, usually the ministry of defence or the ministry of economy, and in some cases, directly with the Procurement Authorities of the Armed Forces.
Offsets/IC come in different shapes and forms, but can generally be divided into two main categories:
- Direct Offsets: Transactions directly related to the defence contract, which usually come in the form of co-production, subcontracting, technology transfer, training, production, licensed production, or financing activities.
- Indirect Offsets: Transactions not directly related to the defence contract, which aim to trigger other technological and industrial advancements in the defence or other sectors, like IT or Telecommunications, by drawing on the multiple areas of knowledge and technology capabilities of the prime contractors, or their subcontractors. Indirect offsets can include purchases, investment, training, financing activities, marketing/exporting assistance, and technology transfer.
Every country has developed its own socioeconomic and political connotation of Offsets/IC by structuring offset regulations that best serve their needs. On the one hand, developed countries with established defence industries use offsets as a way of enhancing product development and market access by placing subcontracting work or infusing advanced technology to their domestic defence or high tech companies. On the other hand, less developed countries use offsets in order to obtain technology and capabilities that do not exist in their current industrial base, as well as establish cooperation and integrate their industry into international supply chain channels. Overall, offset policies greatly differ from country to country and related 'eligible' offset transactions (per country), are mostly selected on a discretionary basis, hence, each offset package can be fairly characterized as 'unique'.